In the context of the ongoing pursuit of high performance and miniaturization in electronic devices, thermal management has become a critical challenge for the industry. Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) has emerged as an ideal thermal management material due to its high thermal conductivity, excellent insulation properties, and superior thermal stability. However, the different morphologies of h-BN—plate-like and spherical—exhibit significantly different performance characteristics in practical applications, directly impacting the efficiency of thermal management systems.
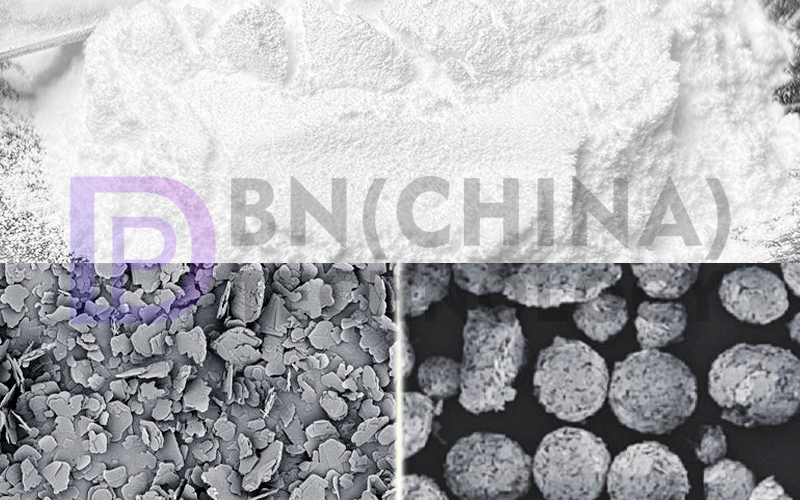
The fundamental difference between plate-like and spherical h-BN stems from their layered crystal structures. h-BN, often referred to as “white graphite,” exhibits pronounced anisotropy in its thermal conductivity: plate-like h-BN demonstrates exceptional thermal conductivity along the horizontal direction but significantly reduced conductivity along the vertical direction, making it more suitable for horizontal heat dissipation scenarios; spherical h-BN, due to its internally interlocked plate crystals, exhibits isotropic thermal conductivity, facilitating heat transfer in multiple directions. In terms of processing, spherical particles have high filling rates and good flowability, making them easier to uniformly disperse in the matrix; plate-shaped fillers, however, tend to agglomerate, increasing system viscosity and limiting filling rates, though they can enhance material mechanical strength.
Different morphologies of h-BN are suitable for different application scenarios. Flake-shaped h-BN tends to align along the flow direction during high-shear processing, forming horizontal heat conduction pathways, making it suitable for applications such as LED heat dissipation substrates and smartphone frames. Its lubricating and insulating properties also make it an ideal choice for high-temperature lubricants and electronic packaging materials. Spherical h-BN, with its isotropy and high fillability, is more suitable for thermal interface materials (such as thermal grease and thermal pads) and battery thermal management systems. It can efficiently conduct heat in the vertical direction while avoiding local overheating, and also meets the low dielectric loss requirements of high-frequency circuits like 5G.
Recent studies have shown that combining flake-shaped and spherical h-BN can overcome the limitations of single-filler materials: the flake-shaped structure acts as a “thermal bridge” to connect spherical particles, reducing thermal resistance gaps and constructing a more efficient three-dimensional thermal conduction network, significantly enhancing overall thermal conductivity.
Additionally, surface modification of h-BN is critical for maximizing its performance. Due to its strong chemical inertness, its surface lacks active groups, leading to poor interface bonding with the substrate and increased thermal resistance. Through modification methods such as hydroxylation, amination, and alkylation, its compatibility and dispersion with different polymer substrates can be enhanced, further optimizing the thermal and mechanical properties of the composite material.
In summary, both plate-shaped and spherical hexagonal boron nitride have their own advantages in thermal management. In practical applications, the choice should be made based on specific heat dissipation directions, processing techniques, and performance requirements. Additionally, synergistic effects can be achieved through morphology composites and surface modifications, providing optimal solutions for thermal management in electronic devices.




